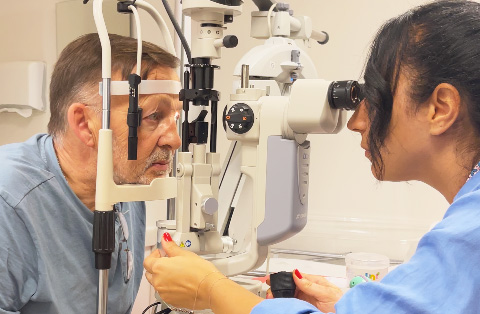
Blurred vision after cataract surgery? YAG laser capsulotomy is a quick, painless solution to restore clarity by treating posterior capsule opacification. Regain sharp, vibrant vision today!
What is YAG Laser Capsulotomy?
YAG laser capsulotomy is a medical procedure used to treat posterior capsule opacification (PCO), a common complication after cataract surgery. PCO occurs when the thin membrane (posterior capsule) that holds the intraocular lens in place becomes cloudy, leading to blurred vision.
The procedure uses a YAG (yttrium-aluminum-garnet) laser to create a small opening in the cloudy posterior capsule. This allows light to pass through clearly, restoring vision. It is a non-invasive, outpatient treatment that is quick and highly effective.
When Do You Need a YAG Capsulotomy?
A YAG capsulotomy is needed when posterior capsule opacification (PCO) develops and begins to interfere with vision. PCO can cause symptoms similar to cataracts, such as blurry or hazy vision, difficulty seeing in bright light, or trouble with daily activities like reading or driving.
This condition does not typically occur immediately after cataract surgery. It may develop weeks, months, or even years later. If your vision problems worsen after cataract surgery and an eye examination confirms PCO, your doctor may recommend a YAG capsulotomy to restore clear vision.
What are the Benefits of Posterior Capsulotomy?
Posterior capsulotomy, specifically using a YAG laser, offers several benefits for individuals experiencing vision problems due to posterior capsule opacification (PCO). These benefits include:
Restoration of Vision
Clears the cloudy posterior capsule, allowing light to pass through to the retina.
Improves visual sharpness and clarity, often restoring vision to levels achieved after cataract surgery.
Quick and Painless Procedure
Non-invasive and typically performed in an outpatient setting.
The procedure is painless, requiring only numbing eye drops and lasting just a few minutes.
Immediate Results
Most patients notice significant improvement in vision within hours or days.
Enhances quality of life by resolving difficulties with reading, driving, or other daily tasks.
Long-Term Effectiveness
The results are usually permanent, as the treated portion of the capsule does not regenerate.
Rarely requires repeat treatments for the same condition.
Low Risk of Complications
Minimally invasive with a low risk of side effects or complications.
Serious complications, such as retinal detachment or pressure elevation, are rare.
Convenience and Cost-Effectiveness
No need for incisions or extensive surgical preparation.
Performed in a clinical setting without requiring hospitalization, reducing costs compared to more invasive procedures.
Posterior capsulotomy is a trusted, effective solution for restoring vision compromised by PCO, with substantial benefits that significantly outweigh the risks.
What Happens During a YAG Laser Procedure?
During a YAG laser capsulotomy, the procedure typically follows these steps:
Preparation: Your eye is numbed with anesthetic eye drops to ensure comfort. A special contact lens may be placed on the eye to help focus the laser.
Laser Treatment: The YAG laser is directed at the cloudy posterior capsule. The laser creates a small opening in the center of the capsule, allowing light to pass through clearly. The procedure is precise and takes only a few minutes.
Post-Treatment: You may be given anti-inflammatory eye drops to use for a few days. Most patients can resume normal activities immediately after the procedure.
The entire process is painless and performed on an outpatient basis.
How Does the Laser Target the Posterior Capsule?
The YAG laser targets the posterior capsule using highly focused bursts of light energy. The procedure begins with the use of a slit lamp microscope, which allows the ophthalmologist to visualize the inside of the eye in detail. The cloudy posterior capsule is identified, and the laser is precisely aimed at this membrane.
The YAG laser delivers short, intense pulses of energy to create a small, circular opening in the capsule. This opening allows light to pass unobstructed to the retina, improving vision. The laser’s precision ensures that surrounding structures, like the intraocular lens and other parts of the eye, remain unaffected.
What to Expect After YAG Laser?
After a YAG laser capsulotomy, most patients notice an improvement in their vision within a few hours to a few days. However, some temporary effects and steps for care should be expected:
Immediate Effects: Your vision might be blurry immediately after the procedure due to the dilating drops used or mild inflammation. This typically resolves within a day.
Follow-Up Care: Your doctor may prescribe anti-inflammatory eye drops to reduce swelling. A follow-up appointment might be scheduled to monitor healing and ensure there are no complications.
Vision Improvement: Clearer vision is usually achieved quickly, often restoring the sharpness lost due to posterior capsule opacification.
Patients can generally resume normal activities the same day, but it is important to follow the specific instructions provided by the ophthalmologist.
What is the Recovery Time for YAG Laser Capsulotomy?
Recovery after YAG laser capsulotomy is generally smooth and uncomplicated. Most patients notice significant improvement in their vision shortly after the procedure. Any mild side effects, such as blurry vision or floaters, typically resolve quickly without impacting normal daily activities.
Immediately After the Procedure: Vision may be blurry due to dilation drops or mild inflammation. Some patients might notice floaters.
Hours Later: Many experience clearer vision as the eye begins to adjust.
First Few Days: Any remaining mild discomfort or floaters typically resolves. Anti-inflammatory drops may be used if prescribed.
One Week: Full recovery is usually achieved, with restored sharp and clear vision.
Follow-Up Visit: A check-up may be scheduled to ensure proper healing and monitor for rare complications.
Possible Side Effects and Complications
YAG laser capsulotomy is generally safe, but like any medical procedure, it carries some potential side effects and complications. These include:
Mild Floaters: Small, shadowy shapes may appear in your vision immediately after the procedure. These are typically temporary and harmless.
Increased Eye Pressure: Some patients experience a temporary rise in intraocular pressure. This is usually monitored and managed by your doctor.
Inflammation: Mild inflammation in the eye may occur but is typically controlled with anti-inflammatory eye drops.
Retinal Detachment: Though rare, the laser treatment can increase the risk of retinal detachment. Symptoms like sudden flashes of light or a curtain-like shadow over your vision should be reported immediately.
Damage to the Intraocular Lens: Improper laser targeting can potentially damage the implanted lens, though this is extremely rare when performed by an experienced ophthalmologist.
Most side effects are minor and resolve on their own or with minimal treatment. Serious complications are uncommon, but regular follow-up with your eye doctor helps ensure early detection and management if they arise.
How Effective is YAG Laser Treatment for Secondary Cataract?
YAG laser capsulotomy has proven to be an effective treatment for posterior capsule opacification (PCO) in various populations, including children. The procedure is particularly beneficial after the implantation of acrylic intraocular lenses (IOLs). In studies evaluating pediatric patients with acrylic IOLs, approximately 70% of eyes maintained a clear visual axis after a single YAG capsulotomy. With additional treatments, the success rate increased to 88%.
The energy required for successful treatment typically ranged between 15 to 700 mJ, depending on the density of the posterior capsule. Although the procedure was effective in most cases, younger patients (under 4 years old) were more likely to experience recurrence of PCO compared to older children, emphasizing the importance of early and adequate management to prevent visual complications.
Complications were infrequent but included transient increases in intraocular pressure, laser marks on the IOL (which were generally insignificant visually), and rare occurrences of IOL dislocation. For many children, the Nd:YAG laser capsulotomy restored clear vision efficiently, confirming its role as a safe, cost-effective, and widely accepted treatment for PCO.
Source: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaapos.2005.10.003
Comparing with Other Laser Treatments
When compared to other laser treatments for ophthalmologic conditions, YAG laser capsulotomy stands out due to its specific application, effectiveness, and safety profile. Below are key comparisons:
1. YAG Laser Capsulotomy vs. Argon Laser Photocoagulation
Purpose: YAG laser is used for treating posterior capsule opacification (PCO), while argon laser photocoagulation is primarily used for retinal conditions such as diabetic retinopathy or retinal tears.
Target Area: YAG laser targets the posterior capsule behind the intraocular lens, whereas the argon laser is directed at the retina.
Safety: Both are minimally invasive, but argon laser can occasionally cause peripheral visual field loss due to its retinal focus, while YAG laser risks are localized to complications like transient intraocular pressure elevation or rare retinal detachment.
2. YAG Laser Capsulotomy vs. Femtosecond Laser for Cataract Surgery
Purpose: Femtosecond lasers assist in the cataract extraction process by creating precise incisions and softening the lens, while YAG lasers treat secondary opacifications after cataract surgery.
Technology: Femtosecond lasers operate at an ultrafast pulse duration with femtosecond precision, making them ideal for incisions. YAG lasers use nanosecond pulses for precise membrane disruption.
Effectiveness: Both are highly effective in their respective areas. Femtosecond lasers improve cataract surgery outcomes, while YAG lasers effectively restore vision compromised by PCO.
3. YAG Laser Capsulotomy vs. Excimer Laser for Refractive Errors
Purpose: Excimer lasers reshape the cornea to correct refractive errors like myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism, while YAG lasers address post-cataract complications.
Precision: Excimer lasers ablate corneal tissue with a precision of micrometers, while YAG lasers create openings in the posterior capsule without affecting adjacent tissues.
Risks: Excimer laser risks include dry eyes or corneal haze. YAG laser complications are rarer, primarily involving retinal detachment or minor pressure spikes.
4. YAG Laser Capsulotomy vs. SLT (Selective Laser Trabeculoplasty)
Purpose: SLT is used to reduce intraocular pressure in glaucoma patients, whereas YAG laser capsulotomy treats PCO.
Mechanism: SLT selectively targets melanin-containing cells in the trabecular meshwork to improve fluid outflow, while YAG lasers disrupt the fibrous posterior capsule.
Outcomes: SLT can require repeat treatments over time, while YAG laser capsulotomy often achieves lasting results in a single session.
Each laser treatment is designed for specific conditions, with YAG laser capsulotomy excelling as a targeted and efficient solution for PCO. Its unique ability to restore vision in a quick, outpatient setting makes it a gold standard for this condition, complementing other laser modalities used in ophthalmology.