Toric IOLs correct cataracts and astigmatism in one procedure, providing sharper vision and reducing dependence on glasses. Discover how this advanced solution improves your quality of life effortlessly!
What is a Toric IOL?
A Toric Intraocular Lens (Toric IOL) is a specialized type of artificial lens used to replace the natural lens of the eye during cataract surgery. It is designed to correct astigmatism, a common refractive error caused by an irregularly shaped cornea or lens.
Unlike standard intraocular lenses, which only address nearsightedness or farsightedness, Toric IOLs have unique optical properties that correct both cataracts and astigmatism in a single procedure. This dual correction provides clearer vision and reduces the need for glasses or contact lenses after surgery.
How Do They Correct Astigmatism?
Toric IOLs correct astigmatism by having different powers in specific meridians of the lens. Astigmatism occurs when the cornea or natural lens has an irregular shape, leading to uneven light refraction and blurry vision. Toric IOLs are precisely aligned during surgery to match the specific curvature of the patient’s cornea.
The lens neutralizes the irregular refraction by redirecting light rays to focus properly on the retina, resulting in sharp, clear vision. This customization ensures that both the cataract and the astigmatism are addressed simultaneously, improving overall visual quality.
Understanding Astigmatism and Its Impact on Vision
Astigmatism is a common vision condition caused by an irregular curvature of the cornea or lens. In a normal eye, the cornea and lens are evenly curved, allowing light to focus precisely on the retina. With astigmatism, the uneven shape causes light to scatter or focus unevenly, resulting in blurred or distorted vision at all distances.
This condition can affect daily activities such as reading, driving, or using digital devices, as it reduces visual clarity. It often coexists with other refractive errors like nearsightedness or farsightedness. Uncorrected astigmatism may lead to eye strain, headaches, and fatigue due to the constant effort needed to focus. Proper correction, such as with Toric IOLs, can significantly improve vision and quality of life.
The Role of Toric IOLs in Astigmatism Correction
Toric IOLs play a crucial role in correcting astigmatism during cataract surgery. Unlike standard intraocular lenses, which only replace the cloudy natural lens, Toric IOLs are specifically designed to address the irregular corneal curvature that causes astigmatism.
These lenses have precise optical zones aligned to counteract the uneven refractive power of the cornea. Surgeons carefully calculate and position the Toric IOL at the correct axis within the eye to ensure optimal alignment. This reduces or eliminates astigmatism, allowing light to focus clearly on the retina.
By addressing both cataracts and astigmatism in one procedure, Toric IOLs enhance vision quality and minimize dependence on corrective eyewear post-surgery.
Comparing Toric Lenses with Traditional Lenses
Toric IOLs and traditional intraocular lenses (IOLs) serve different purposes during cataract surgery. Traditional lenses are designed to replace the clouded natural lens and restore clarity of vision but do not correct astigmatism. Patients with astigmatism who receive traditional IOLs often require glasses or contact lenses after surgery to address the residual refractive error.
Toric IOLs, on the other hand, provide dual benefits. They replace the cataract-affected lens and correct astigmatism, offering sharper vision and reducing the need for additional eyewear. While Toric lenses may have a higher upfront cost, they deliver greater convenience and long-term visual improvement.
Comparison Chart: Toric Lenses vs. Traditional Lenses
Feature | Toric IOLs | Traditional IOLs |
Purpose | Replaces lens and corrects astigmatism | Replaces lens only |
Astigmatism Correction | Yes | No |
Visual Outcome | Clearer vision without glasses for astigmatism | May require glasses for astigmatism |
Customization | Personalized to the patient’s corneal shape | Standard design, no customization |
Cost | Higher | Lower |
Post-Surgery Glasses Need | Reduced or eliminated | Often required for clear vision |
Who Should Consider Toric Intraocular Lens Implantation?
Toric Intraocular Lens (IOL) implantation is ideal for individuals undergoing cataract surgery who also have significant astigmatism. These lenses provide a dual solution by addressing both cataracts and the refractive errors caused by astigmatism. Candidates for Toric IOLs typically include:
Patients with Astigmatism: Those with moderate to severe corneal astigmatism that impacts their visual clarity.
Individuals Seeking Glasses Independence: Patients who want to reduce their reliance on corrective eyewear after cataract surgery.
People with Stable Eye Health: Candidates without other eye conditions, such as severe glaucoma or macular degeneration, which could affect the surgery’s outcomes.
Patients with Realistic Expectations: Those who understand that while Toric IOLs improve vision, some may still need glasses for specific tasks like reading.
A thorough eye examination and consultation with an ophthalmologist are necessary to determine if Toric IOLs are the right choice.
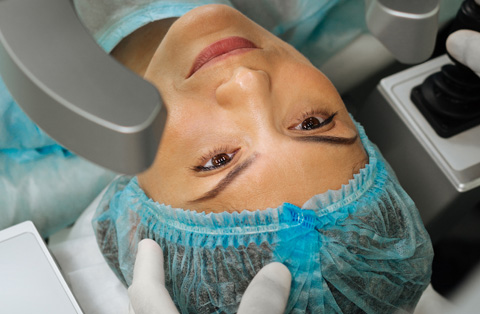
How Is Toric IOL Implantation Performed During Cataract Surgery?
Toric IOL implantation is performed as part of standard cataract surgery, a procedure that typically takes 15 to 30 minutes. The steps include:
Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the eye, ensuring a painless experience.
Small Incision: The surgeon creates a tiny incision in the cornea to access the cataract.
Cataract Removal: Using ultrasound energy (phacoemulsification), the cloudy natural lens is broken into small pieces and removed.
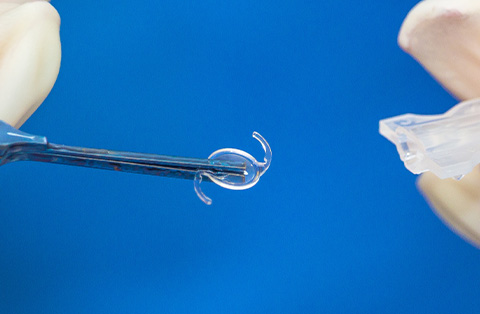
Toric IOL Placement: The Toric IOL, pre-selected based on the patient’s measurements, is inserted into the lens capsule.
Precise Alignment: The surgeon rotates the Toric IOL to align its astigmatism-correcting axis with the patient’s corneal shape, ensuring optimal correction.
Closure: The incision is self-sealing and usually does not require stitches.
The procedure is safe and minimally invasive, with most patients experiencing significant vision improvement within a few days. Post-surgical follow-ups ensure the lens remains properly aligned.
Preoperative Preparation and IOL Calculation
Proper preparation and precise calculations are crucial for successful Toric IOL implantation. The process includes the following steps:
1. Comprehensive Eye Examination
The surgeon evaluates the overall health of the eyes, checking for cataracts, astigmatism, and other conditions like glaucoma or macular degeneration. This ensures the patient is a suitable candidate for Toric IOLs.
2. Corneal Measurements
Advanced diagnostic tools, such as corneal topography or keratometry, measure the curvature of the cornea. These measurements determine the degree and axis of astigmatism, which are essential for selecting and aligning the Toric IOL.
3. Axial Length Measurement
The length of the eye is measured using ultrasound or optical coherence biometry. This helps calculate the power of the intraocular lens needed for optimal vision correction.
4. Lens Selection and Alignment Planning
Based on the data collected, the surgeon chooses a Toric IOL with the appropriate power and astigmatism-correcting properties. Preoperative planning software assists in mapping the ideal alignment of the lens to the eye’s axis.
5. Patient Preparation
Patients are advised to stop wearing contact lenses several days before the measurements, as they can alter corneal shape. In the days leading up to surgery, they may need to use prescribed eye drops to reduce the risk of infection or inflammation.
Accurate preoperative preparation ensures that the chosen Toric IOL will provide clear, balanced vision and long-lasting results.
The Surgical Procedure for Toric IOL Implantation
Toric IOL implantation is performed during cataract surgery, following a standardized yet precision-driven approach to ensure optimal outcomes. The key steps include:
1. Anesthesia and Eye Preparation
The eye is numbed with local anesthesia, often administered as eye drops or a small injection. The area around the eye is cleaned, and a sterile drape is applied to maintain a clean surgical field.
2. Creating the Incision
The surgeon makes a small, self-sealing incision at the edge of the cornea to access the eye’s interior. This incision is carefully placed to minimize astigmatism induction.
3. Cataract Removal
Using a process called phacoemulsification, the cloudy natural lens is broken into small fragments with ultrasound energy and removed through the incision. This step clears the space for the new intraocular lens.
4. Insertion of the Toric IOL
The Toric IOL is folded and inserted through the small incision. Once inside, the lens unfolds and is positioned within the capsular bag, the natural membrane that held the original lens.
5. Precise Lens Alignment
The surgeon rotates the Toric IOL to align its astigmatism-correcting axis with the pre-marked orientation on the eye. This step is critical for the lens to effectively neutralize corneal astigmatism.
6. Final Adjustments and Incision Closure
The surgeon confirms the lens position and makes any final adjustments. The small incision is self-sealing and typically does not require stitches, reducing recovery time.
Postoperative Care and Expectations
Proper postoperative care is essential for a smooth recovery and optimal results after Toric IOL implantation. Patients can expect improved vision within days, though full recovery may take several weeks.
Postoperative Care Guidelines
Medication Use
Patients are prescribed antibiotic and anti-inflammatory eye drops to prevent infection and reduce swelling. These should be used as directed by the surgeon.Eye Protection
A protective shield may be provided to wear while sleeping during the first few nights to prevent accidental rubbing of the eye. Sunglasses can be worn outdoors to reduce sensitivity to light.Activity Restrictions
Patients are advised to avoid strenuous activities, heavy lifting, swimming, or exposing the eye to dust and water for at least one to two weeks. Regular, light activities are generally safe.Follow-Up Appointments
Regular check-ups are scheduled to monitor healing and confirm the proper alignment of the Toric IOL. The surgeon may adjust medications based on recovery progress.
Expectations After Surgery
Immediate Vision Improvement: Vision typically begins to clear within 24–48 hours. However, some initial blurriness or halos around lights may occur as the eye adjusts.
Astigmatism Correction: Patients often experience a noticeable reduction in astigmatism, resulting in sharper, clearer vision.
Mild Discomfort: Some dryness, irritation, or light sensitivity is normal and should resolve within a few days.
Reduced Glasses Dependence: Many patients no longer need glasses for distance vision, though some may require them for close-up tasks like reading.
Adhering to the postoperative care plan and attending follow-ups ensures the best visual outcomes and reduces the risk of complications.
Are There Any Disadvantages or Risks Associated with Toric IOLs?
While Toric IOLs offer significant benefits, they also have potential disadvantages and risks. Understanding these helps patients make informed decisions.
Disadvantages of Toric IOLs
Higher Cost: Toric IOLs are considered premium lenses and may involve additional out-of-pocket expenses, as insurance often does not cover their full cost.
Surgical Complexity: Precise placement and alignment are required to achieve optimal astigmatism correction. This demands advanced surgical expertise.
Residual Astigmatism: In some cases, minor residual astigmatism may remain, especially if the lens shifts post-surgery or if preoperative measurements were slightly inaccurate.
Potential Risks and Complications of Toric IOLs
Lens Misalignment: If the Toric IOL rotates or is not properly aligned, its effectiveness in correcting astigmatism decreases. This may require additional procedures to reposition the lens.
Standard Cataract Surgery Risks: These include infection, inflammation, swelling, bleeding, or increased intraocular pressure. While rare, these risks are present in all cataract surgeries.
Glare and Halos: Some patients may experience visual disturbances such as glare or halos, particularly at night. These symptoms usually improve over time.
Unsuitability for Some Eyes: Patients with certain eye conditions, such as irregular corneal astigmatism or other ocular diseases, may not achieve the desired results with Toric IOLs.
How to Minimize Risks with Expert Surgeon Guidance
Choosing an experienced ophthalmic surgeon is essential to minimize risks and achieve the best outcomes with Toric IOL implantation. Expert guidance ensures precise preoperative planning, accurate lens placement, and proper postoperative care.
Key considerations include:
1. Comprehensive Preoperative Assessment
A skilled surgeon conducts thorough eye examinations to assess the patient’s suitability for Toric IOLs. This includes detailed corneal measurements, axial length calculations, and identifying any preexisting eye conditions that may affect the procedure.
2. Accurate Lens Selection and Alignment
Using advanced diagnostic tools and imaging technology, the surgeon selects the optimal lens power and alignment. Precision mapping ensures the Toric IOL will effectively correct astigmatism and provide clear vision.
3. Surgical Expertise
An experienced surgeon performs the procedure with meticulous attention to detail, ensuring proper placement and alignment of the Toric IOL. Expertise reduces the risk of complications, such as lens misalignment or surgical trauma.
4. Patient Education and Preparation
The surgeon provides clear instructions to prepare the patient for surgery, including discontinuing contact lens use and managing existing eye conditions. Educated patients are better equipped to follow postoperative care guidelines, reducing the likelihood of complications.
5. Postoperative Monitoring
Regular follow-ups allow the surgeon to monitor healing, check the lens alignment, and address any issues promptly. Early detection and intervention help prevent or resolve complications such as lens rotation or residual astigmatism.
Importance of Surgeon Expertise
Choosing a surgeon with a strong track record in Toric IOL procedures ensures a higher level of care and confidence. Patients should inquire about the surgeon’s experience, technology used, and success rates to make an informed decision.
What Advances in Toric Lens Technology Should Patients Know About?
Toric intraocular lens (IOL) technology has evolved significantly, offering improved visual outcomes and greater customization for patients. Key advancements include:
1. Enhanced Design for Stability
Modern Toric IOLs feature advanced designs that improve rotational stability within the eye. This minimizes the risk of lens misalignment, ensuring consistent astigmatism correction over time.
2. Wider Range of Lens Powers
Today’s Toric IOLs are available in a broader range of powers, allowing for the correction of higher degrees of astigmatism. This makes the technology accessible to more patients, even those with complex refractive errors.
3. Premium Multifocal Toric IOLs
Combination lenses, such as multifocal Toric IOLs, correct astigmatism while also addressing presbyopia (age-related near-vision loss). These lenses enhance both distance and near vision, reducing the need for glasses across multiple tasks.
4. Wavefront-Guided Technology
Wavefront-guided Toric IOLs use advanced optics to reduce higher-order aberrations, providing sharper and clearer vision, particularly in low-light conditions.
5. Preoperative Planning Tools
Advancements in diagnostic equipment and surgical planning software help surgeons achieve greater accuracy in lens selection and alignment. Tools like optical coherence tomography (OCT) and corneal topography enhance the precision of measurements.
6. Light-Adjustable Lenses (LALs)
Emerging technologies, such as light-adjustable lenses, allow postoperative adjustments to fine-tune vision. These lenses can be customized after surgery using ultraviolet light to achieve the desired refractive outcome.
7. Improved Materials and Coatings
Modern Toric IOLs are made from biocompatible materials that reduce the risk of inflammation or rejection. Advanced lens coatings minimize glare and halos, improving visual comfort.
Patients considering Toric IOLs should discuss these advancements with their surgeon to understand how new technologies might benefit their specific needs and lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the success rate of Toric IOL?
Toric IOLs have a high success rate, with studies showing a 93–97% reduction in corneal astigmatism for most patients. Approximately 90% of patients achieve uncorrected distance visual acuity of 20/40 or better, significantly reducing their need for glasses. Accurate preoperative measurements, precise lens alignment, and proper follow-up care are key factors influencing these outcomes. Source for further reading.
Which lens is better monofocal or toric?
The choice between monofocal and Toric lenses depends on individual needs. Monofocal lenses correct vision at a single distance but do not address astigmatism. Toric lenses correct both cataracts and astigmatism, providing sharper vision and reducing the need for glasses. Toric lenses are better for patients with astigmatism, while monofocal lenses suit those without it.
What is the cost of a toric lens?
The cost of a Toric IOL varies based on the healthcare provider, location, and specific lens type. On average, Toric lenses cost between $1,500 and $3,000 per eye, in addition to standard cataract surgery fees. Insurance typically covers basic cataract surgery but may not include the cost of premium lenses like Toric IOLs, requiring out-of-pocket payment.
In Turkey, the cost of Toric IOLs is at least 70% more affordable compared to many other countries, making it a cost-effective option for high-quality cataract and astigmatism correction.