What is Breast Reconstruction?
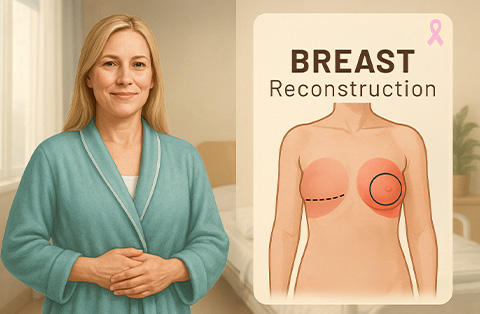
Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure that restores the shape and appearance of one or both breasts after a mastectomy or significant breast tissue loss. It helps patients regain breast symmetry and can improve body image and confidence.
This procedure can be performed using implants, autologous tissue (flaps from the patient’s own body), or a combination of both. Reconstruction can be done immediately after a mastectomy (immediate reconstruction) or delayed until a later time (delayed reconstruction), depending on the patient's condition and preferences.
What Are the Different Types of Breast Reconstruction?
There are two main types of breast reconstruction: implant-based reconstruction and autologous (flap) reconstruction. A hybrid approach combining both methods is also an option.
Types of Breast Reconstruction
Implant-based breast reconstructions
Flap reconstruction
Hybrid approaches
Breast implant reconstructive surgery
Implant reconstruction uses saline or silicone implants to restore breast shape. It is a less invasive procedure and requires less recovery time. In some cases, a tissue expander is placed first to gradually stretch the skin before inserting the final implant. This method works well for patients with enough healthy skin and muscle to support the implant.
One-Stage (Direct-to-Implant) Reconstruction
The implant is placed immediately after the mastectomy, eliminating the need for a tissue expander. This is suitable for patients with enough skin and soft tissue to support the implant.Two-Stage Reconstruction (Tissue Expander Method)
A temporary tissue expander is placed first to gradually stretch the skin. Once the skin is ready, the expander is replaced with a permanent implant. This method is often used when the skin needs more time to adjust after a mastectomy.Pre-Pectoral Implant Placement
The implant is positioned above the chest muscle, reducing pain and recovery time. This technique requires good skin quality and additional support, such as a surgical mesh.Sub-Pectoral Implant Placement
The implant is placed under the chest muscle, providing more coverage and a natural contour. This method may cause more discomfort during recovery due to muscle involvement.
Flap reconstruction
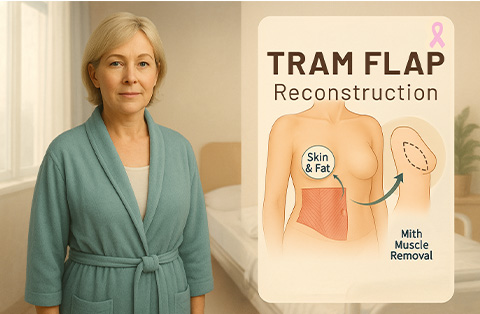
Autologous (flap) reconstruction uses the patient’s own tissue, usually taken from the abdomen, back, or thighs. This technique creates a more natural look and feel but requires a longer and more complex surgery. Common flap procedures include the DIEP flap, which preserves the abdominal muscles while using fat and skin, and the TRAM flap, which takes muscle along with the tissue. The latissimus dorsi flap transfers skin and muscle from the upper back, sometimes combined with an implant for additional volume.
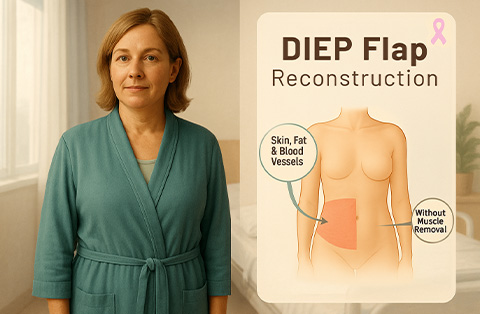
DIEP Flap (Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap)
Uses skin and fat from the lower abdomen while preserving the abdominal muscles. Provides a natural look and feel with less impact on muscle function.TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous Flap)
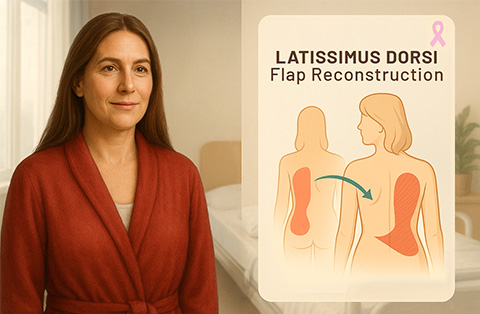
Uses skin, fat, and part of the abdominal muscle. Can be performed as a pedicled flap (staying attached to its blood supply) or a free flap (requiring microsurgery).Latissimus Dorsi Flap
Uses skin, fat, and muscle from the upper back. Often combined with an implant for added volume. Provides good coverage but may cause some muscle weakness.SGAP/IGAP Flap (Superior/Inferior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flap)
Uses skin and fat from the upper (SGAP) or lower (IGAP) buttocks. Suitable for patients who cannot use abdominal tissue.TUG Flap (Transverse Upper Gracilis Flap)
Uses skin, fat, and a small portion of muscle from the inner thigh. Works well for smaller breast reconstruction.PAP Flap (Profunda Artery Perforator Flap)
Uses tissue from the upper inner thigh without taking muscle. Provides a soft and natural breast shape.
Each flap method is chosen based on the patient’s body type, health, and surgical goals.
Hybrid approaches
A hybrid reconstruction combines both implants and autologous tissue to achieve a more natural appearance while maintaining the structure and volume provided by implants. This method is often chosen when there is not enough natural tissue to create the desired breast shape.
Implant + DIEP Flap
Combines a deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap with an implant. The natural tissue from the abdomen enhances the implant’s coverage, creating a softer, more natural breast shape.Implant + Latissimus Dorsi Flap
Uses tissue from the upper back along with an implant. The flap provides additional skin and soft tissue, improving implant support and contour. This is often used when there is not enough skin after a mastectomy.Implant + PAP or TUG Flap
Combines an implant with a profunda artery perforator (PAP) flap or transverse upper gracilis (TUG) flap from the inner thigh. This approach works well for patients with limited abdominal tissue.Stacked Flap with Implant
Uses multiple flaps (such as DIEP and SGAP) along with an implant for added volume. This method is ideal for patients needing more reconstruction but lacking enough tissue from a single donor site.
Hybrid reconstruction offers improved breast shape, texture, and durability by blending natural tissue with implant structure.
Can a Nipple be Reconstructed after Breast Cancer?
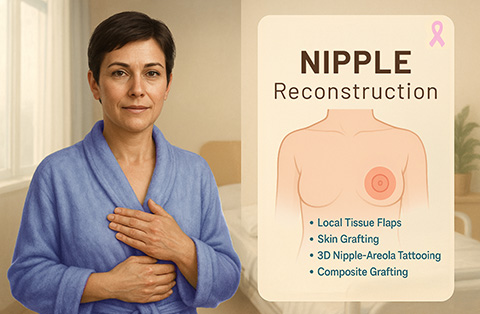
Yes, a nipple can be reconstructed after breast reconstruction. This is usually done as a separate procedure once the breast has healed and settled into its final shape.
Nipple reconstruction typically involves using the patient’s own skin to create a raised nipple. The areola can be restored with medical tattooing to match the natural color. Some patients choose 3D tattooing alone, which creates a realistic appearance without surgery.
Reconstructed nipples may flatten over time, and the sensation is usually limited. However, the procedure can enhance the overall look of the breast and improve body confidence.
How can I Choose the Best Type of Breast Construction Procedure for Me?
The best type of breast reconstruction depends on several factors, including your body type, health, lifestyle, and personal preferences. Your breast surgeon will help guide you based on your specific needs.
If you prefer a shorter surgery with a faster recovery, implant-based reconstruction may be a good option. It requires less initial surgery but may need future implant replacements. If you want a more natural look and feel, autologous (flap) reconstruction uses your own tissue, but it involves a longer procedure and recovery. A hybrid approach, combining implants with natural tissue, may be ideal if you need additional volume but lack enough donor tissue.
Other factors to consider include your overall health, whether you need radiation therapy, and how much scarring you are comfortable with. A consultation with a board-certified plastic surgeon will help determine the most suitable option for you.
How Does Breast Reconstruction Surgery Work?
Breast reconstruction surgery can be performed in one or multiple stages, depending on the chosen method. It is done under general anesthesia and may take several hours.
For implant-based reconstruction, the surgeon places a tissue expander or a permanent implant under the chest muscle or skin. If a tissue expander is used, it is gradually filled over weeks before being replaced with the final implant.
For autologous (flap) reconstruction, tissue from the abdomen, back, thighs, or buttocks is used to create a new breast. This involves microsurgery to reconnect blood vessels and shape the breast.
A hybrid approach combines implants with natural tissue for better volume and contour.
Additional procedures, such as nipple reconstruction or fat grafting, may be performed later to refine the breast shape. Recovery varies, but most patients resume normal activities within a few weeks.
What Can I Expect During the Recovery Time?
Recovery after breast reconstruction varies based on the type of procedure. Most patients stay in the hospital for one to several days. Swelling, bruising, and discomfort are common but improve over time. Pain medication and antibiotics help manage discomfort and prevent infection.
For implant-based reconstruction, recovery is usually faster, with most patients resuming daily activities within a few weeks. Strenuous exercise should be avoided for about six weeks.
For flap reconstruction, recovery takes longer due to the additional surgery at the donor site. Patients may need four to six weeks to heal fully and should avoid heavy lifting or intense physical activity.
Drains may be placed to remove excess fluid and are typically removed within one to two weeks. Wearing a surgical bra provides support and helps reduce swelling. Follow-up appointments ensure proper healing, and scars will fade gradually over time.
What Are the Risks of Breast Reconstruction?
Breast reconstruction is generally safe, but like any surgery, it carries some risks. The complexity of the procedure depends on the method used. Implant-based reconstruction is less invasive, while flap reconstruction involves more extensive surgery.
Possible risks include:
Infection – Treated with antibiotics or, in severe cases, implant removal.
Bleeding or hematoma – Blood may collect under the skin, requiring drainage.
Scarring – All surgeries leave scars, but they fade over time.
Implant complications – Includes rupture, capsular contracture (hardening), or shifting of the implant.
Flap failure – Rare but possible loss of transferred tissue due to poor blood supply.
Changes in sensation – Numbness or reduced sensitivity in the breast or donor site.
Asymmetry – The reconstructed breast may not perfectly match the natural breast.
Regular follow-ups with the surgeon help monitor healing and address any complications early.
Why Choose Breast Reconstruction After a Mastectomy?
Breast reconstruction helps restore the shape and appearance of the breast after a mastectomy. Many patients choose reconstruction to improve body confidence and feel more comfortable in clothing. It can also create symmetry if only one breast was removed.
Some women prefer to avoid wearing external breast prostheses. Reconstruction provides a long-term solution, eliminating the need for removable inserts. Additionally, for those undergoing a unilateral mastectomy, reconstruction can help balance the chest for a more natural look.
While breast reconstruction is a personal choice, it offers both physical and emotional benefits. Consulting with a plastic surgeon can help determine the best approach based on individual needs and preferences.
Benefits of Reconstructing the Breast
Breast reconstruction helps restore the shape and appearance of the breast after a mastectomy. It can improve body confidence and eliminate the need for external prostheses. Many patients feel more comfortable in clothing and experience an enhanced sense of wholeness. Reconstruction also helps balance the chest when only one breast is removed. Modern techniques provide long-lasting and natural-looking results.
Key benefits include:
Restores breast shape and symmetry
Improves self-confidence
Eliminates the need for prostheses
Enhances clothing fit
Balances the chest after unilateral mastectomy
Provides a natural look and feel
Offers long-term results
Frequently Asked Questions
How painful is delayed breast reconstruction?
Pain levels vary based on the type of reconstruction. Implant-based procedures cause mild to moderate discomfort, while flap reconstruction involves more healing time. Pain is managed with medication and improves within weeks. Most patients resume normal activities in four to six weeks. Your surgeon will recommend the best pain management plan for a smoother recovery.
Is breast reconstruction covered by insurance?
Most insurance plans cover breast reconstruction as part of breast cancer treatment. The Women’s Health and Cancer Rights Act (WHCRA) requires coverage for reconstruction after a mastectomy. This includes procedures on the unaffected breast for symmetry. Coverage details vary, so patients should check with their insurance provider to understand costs and eligibility.
How much is breast reconstruction surgery?
The cost of breast reconstruction varies based on the type of surgery, hospital, and surgeon’s expertise. In the USA, the average cost ranges from $20,000 to $50,000, depending on the procedure. In Turkey, prices are at least 70% more affordable while maintaining world-class healthcare quality. Hospital stay, anesthesia, and follow-up care also affect the total cost.
What do reconstructed breasts look like?
Reconstructed breasts look natural but may not feel the same as before. The results depend on the breast surgery technique used. Implants or flap procedures help restore the breast form with symmetry and shape. Nipple reconstruction and 3D tattooing enhance the appearance. Scars fade over time, and final results improve as healing progresses.
When can i sleep on my side after breast reconstruction?
Most patients can sleep on their side about four to six weeks after breast reconstruction. Healing time depends on the surgical method and individual recovery. Sleeping on the back with support is recommended at first. Your surgeon will guide you on when it is safe to change positions based on your healing progress.
Do reconstructed breasts look natural?
Reconstructed breasts can look very natural, especially with advanced techniques. Flap procedures using natural tissue create the most realistic results. Implants also provide a good shape but may feel firmer. Nipple reconstruction and 3D tattooing enhance appearance. Final results improve as swelling decreases, and scars fade over time, giving a more natural look.